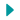
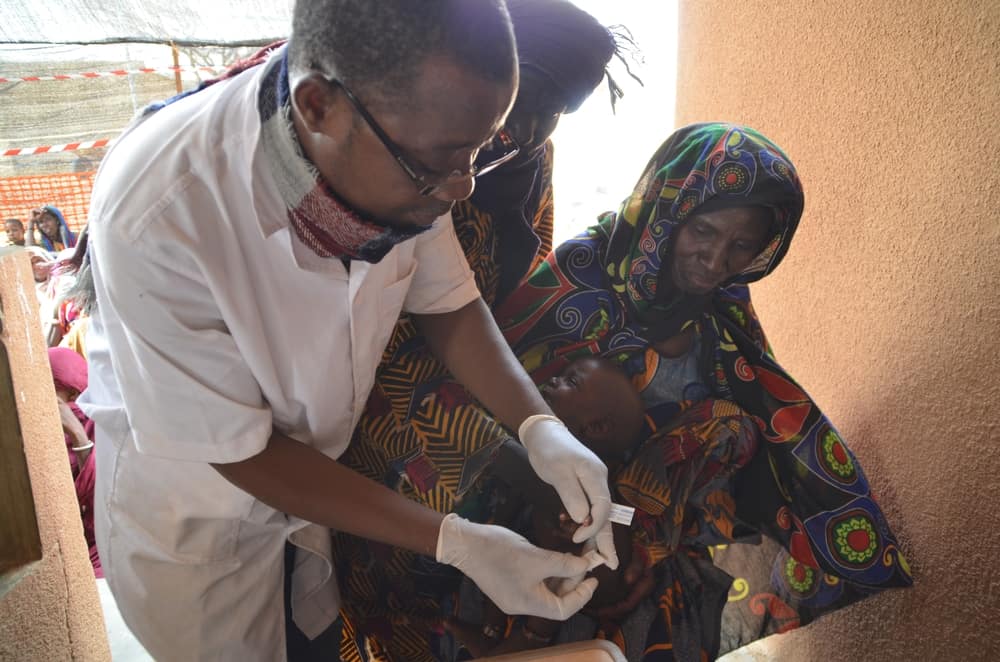
 Aurelie Baumel/MSF
Aurelie Baumel/MSFMédecins Sans Frontières (MSF) is an international, independent, medical humanitarian organisation that delivers emergency aid to people affected by armed conflict, epidemics, natural disasters and exclusion from healthcare. MSF offers assistance to people based on need, irrespective of race, religion, gender or political affiliation.
Our actions are guided by medical ethics and the principles of neutrality and impartiality.
A worldwide movement
MSF was founded in Paris, France in 1971. Its principles are described in the organisation’s founding charter. It is a non-profit, self-governed organisation.
Today, MSF is a worldwide movement of 21 sections, 24 associations and various other offices. They are bound together by MSF International, based in Geneva, Switzerland, which provides coordination, information and support to the MSF Movement.
Thousands of health professionals, logistical and administrative staff – most of whom are hired locally – work on programmes in some 69 countries worldwide.
Humanitarian action
MSF’s work is based on humanitarian principles. We are committed to bringing quality medical care to people caught in crisis, regardless of race, religion or political affiliation.
MSF operates independently. We conduct our own evaluations on the ground to determine people’s needs. More than 90 per cent of our overall funding comes from millions of private sources, not governments.
MSF is neutral. We do not take sides in armed conflicts, we provide care on the basis of need, and we push for independent access to victims of conflict as required under international humanitarian law.
Bearing witness and speaking out
MSF medical teams often witness violence and neglect in the course of their work, largely in regions that receive scant international attention.
At times, MSF may speak out publicly in an effort to bring a forgotten crisis to public attention, to alert the public to abuses occurring beyond the headlines, to criticise the inadequacies of the aid system, or to challenge the diversion of humanitarian aid for political interests.
Quality medical care
MSF rejects the idea that poor people deserve third-rate medical care and strives to provide high-quality care to patients. In 1999, when MSF was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize, the organisation announced the money would go towards raising awareness of and fighting against neglected diseases.
Through the Access Campaign, and in partnership with the Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative, this work has helped lower the price of HIV/AIDS treatment and stimulated research and development for medicines to treat malaria and neglected diseases like sleeping sickness and kala azar.